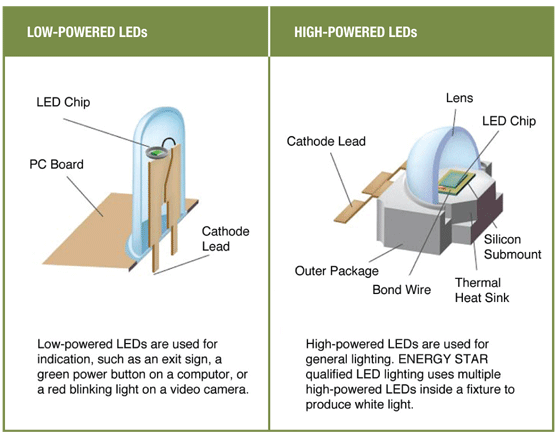
Types of LED and Their Applications
What Does Unilumin Do in the LED Manufacturing Industry?
LED lighting products have become increasingly popular over the last few years, as they tend to be much more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs. In understanding the way in which LED lighting products function, it is important to recognize that the useful life of such products differs from compact fluorescent lighting and incandescent lighting. One of the reasons that LED products are considered to be more efficient than other lighting products is that they do not usually fail or burn out. Over time, an LED product may experience a phenomenon known as lumen depreciation. This occurs when the LED brightness begins to slowly diminish over a period of time. Consequently, the lifetime of an LED product is rated based on predictions regarding when the output of light from the product will decrease by a certain percentage.
The term LED stands for light emitting diode. It is a type of semiconductor that produces light through the passage of an electric current through the device. When the electron particles carrying the current combine with the material in the semiconductor, known as electron holes, energy is released. This energy occurs in the formation of photons.
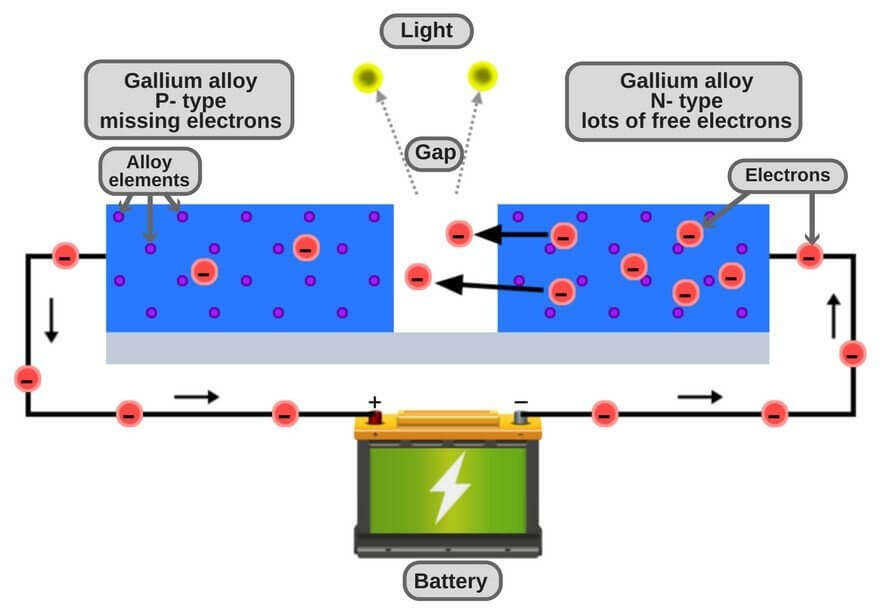
The above diagram shows how the light-emitting diode works and the step by step process of the diagram. From the diagram, we can observe that the N-type silicon is in red color and it contains the electrons, they are indicated by the black circles, while P-type silicon is in the blue color and it contains holes, they are indicated by the white circles.
Firstly, the power supply across the p-n junction makes the diode forward biased, pushing the electrons from n-type to p-type. Pushing the holes in the opposite direction. Secondly, electron and holes at the junction are combined. Finally, the photos are given off as the electrons and holes are recombined. And this is the light emission’s principle of the LED.
It is not uncommon for many people to believe that LED lighting technology was invented in the 21st century. In reality, the history of LED technology actually dates back to shortly after the turn of the 20th century. An English researcher working for Marconi Labs discovered electroluminescence in 1907. Twenty years later, the first LED was created by Oleg Losev, a Russian inventor. While the discovery was important, scientists were not able to obtain a practice use for it until many decades later. In fact, it was not until the early 1960s that a patent was filed for one of the first LED products, following research at Texas Instruments. Within just a few years, multiple laboratories were working on producing an LED capable of producing visible light.
The first yellow LED was produced in 1972; however, most LEDs produced in the early days of the technology were red and used as indicator bulbs. This was largely due to the fact that the light output from the early LED bulbs simply was not bright enough for illumination. Eventually, additional colors would become available, making the technology more applicable to other equipment.
LED technology offers a number of critical benefits to many industries today. Among the most important advantages of LEDs is the consumption of less electricity. Along with saving electricity, LEDs are also considered safer than other lighting choices, including incandescent lights. This is because LED bulbs are actually cooler to the touch, which can reduce the risk of burns when touching the bulbs and even reduce the risk of combustion.
When compared to more traditional lighting sources, LED also offers more longevity. An LED bulb is capable of producing at least 50,000 hours of lighting. Not only do LED bulbs last longer, but they also have less of an impact on the environment. There are no toxic materials used in the production of LED bulbs and they are completely recyclable.
While incandescent bulbs are produced from glass, LED bulbs are produced from epoxy. For this reason, LED bulbs are far less likely to break than their glass counterparts. Furthermore, LED bulbs last much longer than other options. Finally, LEDs are also usually much easier to install.
LEDs offer a variety of uses in many industries. Among the most common applications for LEDs is as household lighting; however, LEDs may also be used for lighting in other industries, such as traffic lights, industrial lighting, and much more. This technology is also used to provide floor lighting in movie theaters and airplanes.
LEDs may also be used for display and indictor purposes on such devices as televisions and smartphones. LED bulbs are preferred for use in displays due to their ability to provide excellent image quality combined with higher brightness, better contracts, and a much faster rate of refresh.
The medical industry has also begun widespread use of LEDs in a variety of applications. Among these applications include light therapy to treat such conditions as neonatal jaundice, eczema, acne, and psoriasis.
The agricultural industry has also begun to use LEDs for the purposes of grow lights.
LEDs are also used in a variety of other applications, including modular lighting, refrigerated case lighting, outdoor and walkway lighting, parking garage lighting, street lights, task lighting, and much more.
While the early production of LED technology may have been somewhat limited, over the years this technology has grown significantly. The growth of this technology has included expanded usage of LEDs by color, brightness, and even types of LEDs now available.
The first LED to be produced was yellow, but as research continued, this led to the production of LEDs in a rainbow of colors. Today, LEDs are available in a variety of colors and different colors of LED bulbs often now offer a variety of uses.
For instance, red LEDs are frequently used in applications that call for the recognition of safety and caution. As such, red LED bulbs may be used in traffic lights as well as indicator lights. The usage of red LED bulbs is not limited to the safety industry, however. Red has long been associated with the food industry. Consequently, red LED are often used in restaurants, bars, and clubs.
Since the color blue often evokes a sense of calm and peace, blue LEDs may be used in bathrooms and bedrooms as well as in any situation when there is a need to provide a peaceful environment. Such bulbs may also be useful for nighttime reading situations.
White LED bulbs are often used in situations that require basic illumination. This type of bulb is often used in situations when there is a need to create a contrast between colors.
LEDs may also be used in applications according to the level of brightness produced.
These LEDs are typically used in low-light environments or for subtle lighting effects. They are often used in indicators, backlights, and decorative lighting. While they may not produce the same intensity as high-brightness LEDs, they can be more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan.
These LEDs offer a balance between brightness and power consumption. They are commonly used in various applications, including automotive lighting, general lighting, and signage. Medium-brightness LEDs are suitable for a wide range of tasks and provide a good compromise between performance and efficiency.
Also known as COB (Chip-on-Board) LEDs, these LEDs are designed to deliver intense light output. They are often used in applications that require bright illumination, such as floodlights, stage lighting, and architectural lighting. High-brightness LEDs are capable of producing powerful beams of light and are well-suited for large-scale projects.
These LEDs are the most powerful available and are used in applications that demand extreme brightness. They are commonly found in high-powered lighting systems, such as stadium lighting and industrial applications. Ultra-high-brightness LEDs offer exceptional light output but require careful heat management to prevent damage.
RGB LEDs refer to red-green-blue LEDs. These types of LEDs contain three different LEDs in one device. They are not limited to producing just three colors, however. Due to the fact that these three colors are the primary colors, they can be used for producing a variety of different hues.
SMDs refer to surface mount LEDs. They are not a specific type of LED but instead refer to a type of packaging that is available in a variety of different sizes ranging from large to extremely small. The much smaller devices can be more difficult with which to work, but in situations where space is limited, they can be an ideal solution.
High-power LEDS are known for producing incredible levels of brightness. LEDs are typically considered to be a high-power device if they are capable of emitting at least one watt of power. While these types of LEDs are used in everyday devices such as flashlights, they can also be combined in arrays for use in auto headlights and spotlights. Due to the amount of power making its way through this type of LED, a heatsink is frequently required. Heatsinks work to transfer heat waste.
OLED refers to an Organic Light-Emitting Diode. This type of technology involves the use of organic molecules to produce lights. A backlight is not required in these types of emissive displays. As a result, OLEDs are more efficient and thinner than traditional LCD displays. Along with offering improved image quality, OLEDs also offer the benefits of being more flexible, and transparent. This flexibility means they can be folded, rolled, and stretched.
LEDs are also available in much smaller sizes. These mini LEDs can be used to create exciting displays of lights with improved contrast ratios, energy efficiency, and brightness.
Focusing on products and technology innovation, Unilumin is one of the first group of companies in the LED display industry to lead the technology trend of fine pitch, LED super TV, mass production of Mini LED 0.9, etc.
Unilumin's Mini LED displays exemplify the pinnacle of LED technology. These products offer a harmonious blend of exceptional picture quality, versatility, and reliability. With features such as micro-pitch designs, deep black levels, high brightness, wide viewing angles, and energy efficiency, Unilumin's Mini LED displays cater to a diverse range of applications, from home cinemas to professional environments.

Unilumin's LED displays and solutions are widely used in security monitoring centers, military command centers, emergency command centers, broadcasting, energy dispatch systems, communications, transportation, sports events, public safety, etc. There’re many classic cases at home and abroad, such as Outdoor Screen of China's 60th Anniversary Celebration Tiananmen Square, Shanghai World Expo, Shenzhen Universiade, London Olympics, Brazil Olympics, The 20th anniversary of Hong Kong's return Garrison Hall, 2018 Russia World Cup and other classic cases.


The invention and breakthrough applications of LED represent the progress and innovation of the society, which is also the reason and motivation for Unilumin to attach great importance to technological advancement in LED products and solutions.